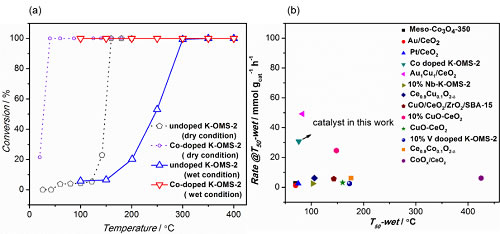
The catalytic oxidation of CO involves many fields such as tobacco reduction, automobile exhaust purification, gas masks, CO gas detectors and fuel cells. Therefore, the development of CO oxidation catalysts has always been one of the research hotspots in the field of catalysis. Although noble metal catalysts have excellent performance, they are expensive and have limited market applications. In contrast, non-precious metal catalysts have received extensive attention due to their low price and good catalytic activity. However, such catalysts are very sensitive to the presence of water vapor in the real application environment, and metal active sites are easily covered by water molecules and quickly deactivated. Therefore, how to maintain high catalytic performance in the real environment where water vapor exists is still a key technical difficulty. In order to solve the above problems, the non-precious metal catalytic material research team of the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, used a one-step hydrothermal synthesis method to successfully introduce cobalt and other transition metal elements into the framework of K-OMS-2 to prepare Co-OMS. -2 molecular sieves. Studies have shown that the doped Co-OMS-2 has a nanofibrous morphology and the specific surface area increases from 70.6 m2/g to 188.3 m2/g (Fig. 1). The cobalt ion replaces the framework manganese ion, enhances the mobility of reactive oxygen species, and improves the reduction performance of OMS-2. In addition, the doping of cobalt makes the surface of the OMS-2 catalyst more hydrophobic. The CO oxidation performance of this catalyst was evaluated (Figure 2, Figure 3). Under anhydrous conditions, the CO conversion reached 100% at 30°C, and the reaction rate was 67 mmol g-1 h-1 at 60°C. It is 28.8 times the reaction rate of the undoped OMS-2 catalyst. When 3% water vapor was introduced into the reaction gas, the Co-OMS-2 catalyst was maintained at 100% at 100°C and above. By comparison with Au/CeO2, Pt/CeO2 and Au1Cu1/CeO2 and other noble metal catalysts, the resistance of Co-OMS-2 catalyst is compared with parameters such as T50 (reaction temperature of 50% conversion) and reaction rate at this temperature (Fig. 2b). Water performance is no less noble metal catalysts. This work provides a theoretical basis for the industrial production of efficient and cheap purification of new CO materials. The relevant results were published as cover articles in the ChemCatChem journal (2017, 9, 1163-1167, DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201601681). The above work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51422212), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21403261 and 21307142), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LR16B030001) and the Henan Zhongyan Industrial Co., Ltd. (ZW2014052). Funding. Figure 2. (a) Catalytic oxidation of CO with OMS-2 and Co-doped OMS-2; (b) Water resistance comparison with Au/CeO2, Pt/CeO2 and Au1Cu1/CeO2 noble metal catalysts in the literature. Handle Magnetic Box are made of super strong neodymium magnetic systme inside of the steel case. It can be activated by simply pressing down the button by the hand or foot. To deactivate them, the magnets are easily release by handle. In the inactive position, the Shuttering Magnets can be easily removed from the table form. The precast concrete magnets could be used alone or connected with adpator to fix the formwork. Magnetic Box With Handle,Handle Shuttering Magnets,Handle Precast Magnet Box,Handle Precast Concrete Magnet Ningbo Shine Magnetic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.shutteringmagnetic.com
Figure 1. Morphological comparisons: (a) OMS-2; (b) Co-doped OMS-2