Pipe Black Pipe,Black Pipe,Iron Pipe Xinpengyuan Metal Manufacturing Co., Ltd , http://www.lc-steelpipe.com
Among the pressure valves of industrial pipelines, cast steel valves are widely used due to their economical cost and design flexibility. However, as the casting process is constrained by casting size, wall thickness, climate, raw materials and Construction operations, various casting defects such as sand holes, pores, cracks, shrinkage, shrinkage holes and inclusions may occur in the casting, especially in sand casting alloys. Steel castings are more. Because the more alloying elements in the steel, the worse the fluidity of the molten steel, the casting defects are more likely to occur. Therefore, the identification of defects and the development of a reasonable, economical, practical and reliable repair welding process to ensure that the valve after repair welding meets the quality requirements has become a common concern of valve hot and cold processing. This article describes the repair welding methods and experience of several common steel casting defects (the welding rod is indicated by the old grade).
2, defect processing
2.1, defect judgment
In production practice, some casting defects do not allow repair welding, such as penetrating cracks, penetrating defects (bottoming), honeycomb vents, slag inclusions that cannot be removed, and shrinkage of more than 65 cm2, and contracts between the two parties. Other major defects that cannot be repaired in the agreement. The type of defect should be judged before repair welding.
2.2, defect rejection
In the factory, a carbon arc gouging is generally used to blow the casting defects, and then the defective portion is polished with a hand angle grinder to expose the metallic luster. However, in the production practice, it is more necessary to directly remove the defects with a large current of the carbon steel electrode and to grind the metal luster with an angle grinder. Generally, the casting defects are removed. The <4mm-J422 electrode, 160~180A current can be used to remove the defects. The angle grinder grinds the defect into a U shape to reduce the welding stress. The defect is thoroughly removed and the repair welding quality is good.
2.3, preheating of defective parts
Carbon steel and austenitic stainless steel castings, where the area of ​​the repaired joint is <65cm2, the depth <20% or 25mm of the thickness of the casting, generally does not require preheating. However, pearlitic steel castings such as ZG15Cr1Mo1V and ZGCr5Mo have preheating due to the large hardening tendency of steel and cold welding, and the preheating temperature is 200-400 ° C (fixed by stainless steel welding rod, the temperature is small). The holding time should be no less than 60 minutes. If the casting can not be preheated as a whole, the oxygen-acetylene can be heated to 300-350 °C after the defect is extended by 20 mm (the dark red is visually observed in the dark place), and the large torch neutral flame gun is first made at the defect and the periphery. The circumference is swiftly swung for a few minutes, then slowly moved for 10 min (depending on the thickness of the defect), so that the defect is fully preheated and repaired quickly.
3, repair welding method
The current and electrode for repair welding of defects are shown in Table 1. 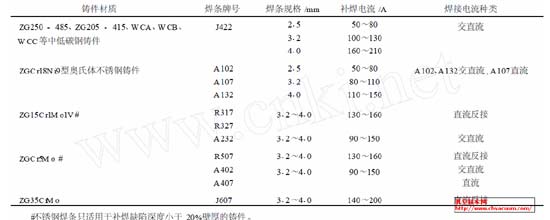
3.1, requirements
When repairing austenitic stainless steel castings, it should be cooled in a ventilated place. For pearlite low alloy steel castings and carbon steel castings with excessive repair welding area, the leeward or the windshield should be selected to avoid cracks caused by rapid cooling. If one layer is repaired, the dross should be removed immediately after repair welding, and hammered evenly outward along the center of the defect to reduce the repair stress. If the repair welding is carried out in several layers (generally 3 to 4 mm is a repair layer), the glue residue and the hammer repair welding area should be removed in time after each layer repair welding. For example, in the winter welding, ZG15Cr1Mo1V pearlite alloy steel castings, each layer of repair welding is also applied with repeated heating of oxy-acetylene, and then quickly repair welding to avoid welding cracks.
3.2, electrode processing
Before repair welding, first check whether the welding rod is preheated. Generally, the welding rod should be dried at 150~250°C for 1h. The preheated electrode should be placed in the incubator for easy use. The electrode is repeatedly preheated 3 times. If the surface of the electrode is peeled off, cracked and rusted, it should not be used.
3.3, the number of repair welding
Pressure-bearing castings, such as valve shells, are subjected to pressure-testing, and the same part is generally only allowed to be repaired once. It is not possible to repeat the repair welding, because multiple repairs will make the grains in the steel coarse, affecting the bearing performance of the casting, unless the casting can The heat treatment is repeated after the welding. For other repair welding of the same part without pressure, it is generally recommended that the repair welding does not exceed 3 times. The carbon steel castings with the repair welding of more than two times in the same part shall be treated with stress relief after welding.
3.4, repair layer height
The repair welding height of castings is generally about 2mm higher than the casting plane to facilitate machining. The repair layer is too low, and it is easy to expose the solder after machining. The repair layer is too high, time-consuming and labor-intensive materials.
4, after welding repair
4.1, important repair welding
The hydraulic test has a leakage casting, a casting with a repair area of ​​>65 cm2, and a casting with a depth of 20% or 25 mm, which is considered to be an important repair welding in ASTM A217/A217M-2007. It is proposed in this important repair welding A217 standard that stress relief treatment or complete reheat treatment should be carried out, and this stress relief treatment or complete reheat treatment must be carried out by a qualified method, that is, important repair welding needs to be formulated. Repair welding process. ASTMA 352/A352M2006 stipulates that stress relief or post-weld heat treatment after important repair welding is mandatory. In China's industry standard JB/T5263-2005 corresponding to A217/A217M, important repair welding is defined as “heavy defectâ€. But in fact, in addition to the casting blank can be completely reheated, many defects are often found in the finishing process, and can no longer be completely heat treated. Therefore, in production practice, it is usually solved by an experienced welder holding a welding certificate for a pressure vessel on site in an effective manner.
4.2, eliminate stress
After repairing the defects found after finishing, it is impossible to do the overall stress relief tempering treatment. Generally, the partial heat tempering method of the oxygen-acetylene flame in the defect part can be used. Use a large torch neutral flame to swing back and forth slowly, and heat the casting to the surface to appear visible dark red (about 740 ° C), heat preservation (2min / mm, but not less than 30min). Asbestos sheets should be placed on the defects immediately after stress relief. Defects in the diameter of the pearlite steel valve, the asbestos board should be filled in the inner cavity of the through-hole during the repair welding to make it slow. This kind of operation is simple and economical, but requires the welder to have some practical experience.
Stainless steel castings are generally not treated after repair welding, but should be welded in the ventilated place to make the repair welding zone cool. Unless repaired after welding indicates that it has caused a change in austenite structure, or is a heavy defect. The solution treatment should be redone under the contract and conditions. Carbon steel castings and various pearlite castings with excessively large defect areas are in the stage of castings and, although they are rough-processed, but have a finishing allowance, stress-relieving should be applied after repair welding. The carbon steel stress relief tempering temperature can be set to 600 ~ 650 ° C, ZG15Cr1Mo1V and ZGCr5Mo tempering temperature can be set to 700 ~ 740 ° C, ZG35CrMo tempering temperature is set to 500 ~ 550 ° C. For all kinds of steel castings, the holding time for stress relief and tempering is not less than 120min, and the furnace is cooled to below 100 °C.
4.3, non-destructive testing
For the "heavy defects" and "important repair welding" of valve castings, the ASTM A217A217M-2007 standard stipulates that if the casting production meets the requirements of S4 (magnetic powder inspection) supplementary requirements, the repair welding shall be checked by the magnetic particle inspection of the same quality standard for inspection of castings. . If the casting production meets the requirements of the S5 (radiography inspection) supplementary requirements, the castings leaking for the hydraulic pressure test, or any castings with a depth of more than 20% of the wall thickness or 1 in1 (25 mm), and the preparation for repair welding Any repair welding of castings with a pit area greater than 10 in2 (65 cm2) shall be inspected by inspection of the same standard ray inspection of the casting. The JB/T5263-2005 standard stipulates that ray or ultrasonic testing should be performed after repair of heavy defects. That is, for heavy defects and important repair welding, effective non-destructive inspection must be carried out, and it can be used only after passing the certification.
4.4, rating
For the grade of non-destructive inspection defect report in the repair welding area, JB/T3595-2002 stipulates that the groove and repair welding position of the steel casting valve of the power station valve shall be assessed according to GB/T5677-1985, and the third grade is qualified. The butt weld of the valve shall be assessed according to GB/T3323-1987, and the second grade shall be qualified. In JB/T644-2008, two different grades of defects in the castings are also clearly defined. When there are two or more types of defects with different grades in the assessment area, the lowest grade is determined as the comprehensive rating. . When there are two or more types of defects with the same level, the comprehensive level should be reduced by one level.
For slag inclusion, unmelted and incomplete penetration of defects in the repaired zone, JB/T6440-2008 stipulates that it can be regarded as the slag inclusion of casting defects, and the porosity of the defect in the repaired zone can be regarded as the evaluation of the porosity of the casting defect. .
The ordering contract of the general working condition valve does not indicate the grade of the valve casting, and the qualification level after the defect repair is indicated in the contract. This often brings many contradictions to the production, inspection and sales of the valve. According to the actual quality level and years of experience of China's current steel castings, the level of repair welding area assessment is generally considered to be no less than the third level in GB/T5677-1985, namely the level III specified in the ASMEE446b standard. The pressure bearing parts of cast steel valves and high-pressure cast steel valves in acid-resistant and corrosion-resistant pipelines should generally reach ASMEE446bII or above. The results of the ray inspection show that the defect generated during the welding process is less than the casting itself and the level is higher after the defect area conforming to the standard procedures and specifications. In short, repair welding as part of the manufacturing process, can not be taken lightly.
4.5, hardness test
Although the repair welding zone is qualified by non-destructive testing, if it is necessary to machine, the hardness of the repairing zone should be checked again. This is also an inspection of the effect of stress relief. If the tempering temperature is not enough, or the time is insufficient, the deposited metal in the repaired welding area will have high strength and poor plasticity, and the welding area will be very hard during machining, which may easily cause the tool to crack. The properties of the base metal and the deposited metal are inconsistent, and it is easy to cause local stress concentration, and there is a clear trace of the transition boundary of the repair welding. Therefore, the repair welding area needs to be identified and detected by the hardness value. Gently grind the repaired area with a hand grinder, hammer the three points with a portable Brinell hardness tester, and compare the hardness of the repair weld zone with the hardness of the steel casting itself. If the hardness values ​​of the two regions are similar, it indicates that the oxy-acetylene tempering is basically successful. If the hardness of the repair weld zone is greater than 20 hardness of the steel casting, it is recommended to rework until the hardness is close to the base metal. The hardness of the pressed steel castings after heat treatment is generally designed to be 160-200HB, and the hardness is too low or too high, which is not conducive to machining operations. The hardness of the repair pad is too high, which will reduce the plasticity and reduce the safety performance of the valve housing.
5 Conclusion
Scientific repair welding of steel casting defects is an energy-saving remanufacturing engineering technology. With the cooperation of modern testing methods, innovations should be continuously made in the repair welding tools, welding consumables, personnel and processes to truly realize the integration of manufacturing and maintenance.
1 Overview