The Poleline fastener, also known as a Poleline Hardware or poleline fitting, poleline fastener is a device used to secure electrical power lines to utility poles or transmission towers. Poleline fasteners is designed to provide strength, stability, and proper alignment for the power lines,ensuring pole line safe and reliable operation. Poleline Hardware or Power line accessories , poleline fitting widely used in connecting, handling and holding various overhead line systems, insulators, wires, and other utilities. Poleline fastener is an important component of the pole line construction. According to the application, poleline fastener can be divided into Telecommunication pole hardware, Utility pole mounting hardware, Transmission and Tower hardware. Yokelink supply a full line of Poleline Hardware, We offer from the top of the pole to underground. Double Arming bolt, Oval Eye bolt, MF Lock nut, Thimble Eyebolt, Poleline Fastener Ningbo Yokelink Machinery Co.,Limited , https://www.yokelink.comWhat is poleline fastener
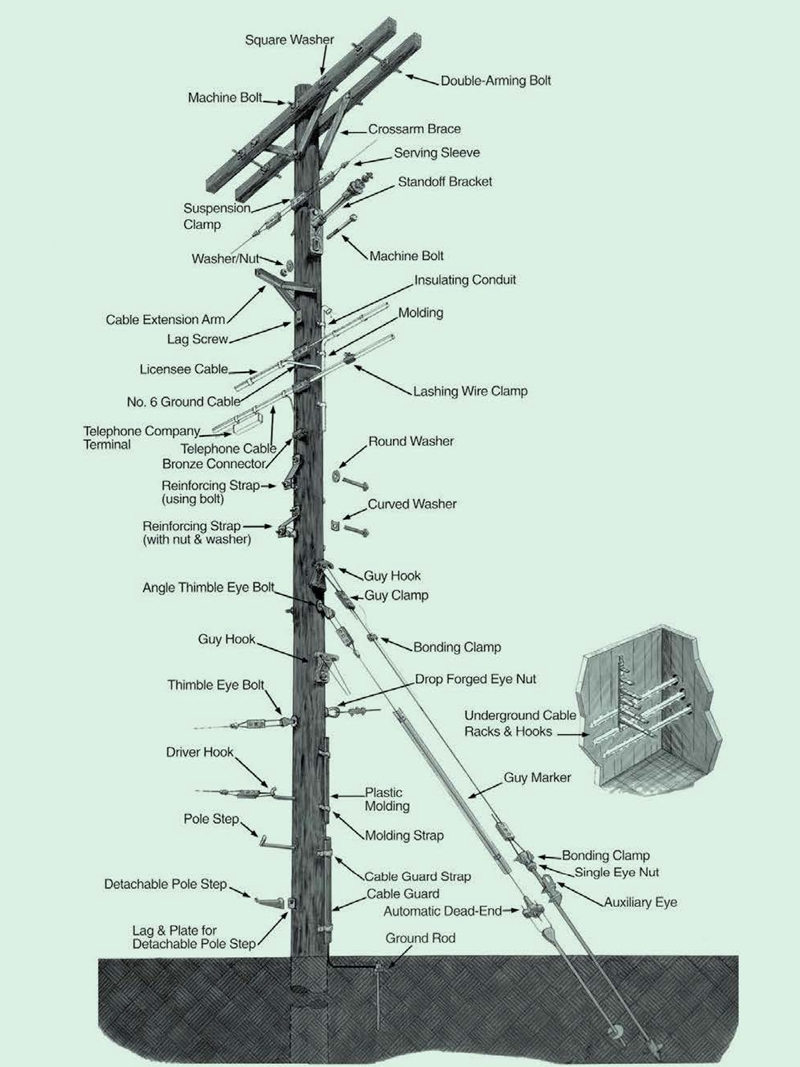
Application of Poleline Fastener
Type of Poleline fastener for utility pole
Yokelink Poleline Fastener
The mining industry has been experiencing a cooling trend for decades, and in recent years, the world's top three mining companies have announced significant spending cuts. Brazilian iron ore giant Vale recently revealed that its capital expenditure budget for next year will drop from $16.3 billion this year to $14.8 billion, marking its third consecutive year of reductions. This is the lowest level of spending since 2010, reflecting the impact of declining iron ore prices over the past two years.
BHP Billiton and Rio Tinto, the other two major iron ore producers, have also taken similar steps by selling non-core assets to cut costs. BHP Billiton announced that its spending this year will fall below $15 billion, down from $21.7 billion last year. Meanwhile, Rio Tinto plans to make further cuts after achieving a $2 billion reduction this year. The company is prioritizing debt repayment and cost control as it faces rising net debt, which reached over $19 billion last year.
Analysts suggest that these spending cuts are part of a strategic move to improve profitability amid a slowing global demand for iron ore. “The golden decade of steel is over, and mine profits are not as strong as they used to be,†one expert noted. China’s long-term de-capacity policy in the steel sector is expected to reduce iron ore demand, putting additional pressure on the big miners.
Vale’s CEO, Murilo Ferreira, emphasized efforts to lower production costs and focus on higher-margin mines to boost shareholder returns. Similarly, Rio Tinto’s CEO Sam Welsh stated that the company will continue to reduce capital expenditures. Since 2012, Rio Tinto has laid off thousands of workers and sold assets to streamline operations.
BHP Billiton also hinted at keeping annual spending under $15 billion, following a significant cut in the fiscal year ending June 2014. The company plans to maintain this strategy in the coming years.
Looking ahead, analysts predict that global iron ore supply will outpace demand due to new mine capacities coming online between 2014 and 2015. Vale’s head of iron ore strategy, Jose Carlos Martins, warned that by 2018, iron ore production could exceed demand by 5% to 6%, with global output potentially reaching 1.6 billion tons by 2020—far above expected consumption levels of 1.5 billion tons.
With the shift toward index pricing and increased overseas equity investments in China, the dominance of the three major mining companies is being challenged. This ongoing transformation signals a difficult period for the industry as it adapts to a more competitive and cost-conscious market.
Poleline Fastener